Configure Snmp Windows 7 Cacti Monitoring Average ratng: 6,3/10 8373reviews
What Is SNMP How To Install Configure SNMP in Linux. Simple Network Management Protocol SNMP is an internet standard protocol which can be used to remotely retrieve the operational statistics of the routers and firewalls. Devices that typically support SNMP include routers, switches, servers, workstations and more. The monitoring tools such as MRTG, cacti uses SNMP to retrieve information from the routers to draw the graphs. How hard can this be I want to get the current CPU performance from a remote Win 2k3 machine. I need to use SNMP because the machine is behind a firewall. In this article, we will go through the installation and simple configuration of SNMP on Linux Cent. OS 7, Ubuntu 1. 6. Basics concepts. SNMP is a protocol that is implemented on the application layer of the networking stack. It is one of the widely accepted protocols to manage and monitor network elements. The protocol was created as a way of gathering information from very different systems in a consistent manner. Configure Snmp Windows 7 Cacti Monitoring ToolsIn general, a network being profiled by SNMP will mainly consist of devices containing SNMP agents. An agent is a program that can gather information about a piece of hardware, organize it into predefined entries, and respond to queries using the SNMP protocol. SNMP requires only a couple of basic components to work Managed device it is a computer that is configured to poll SNMP agent for information. It can be any machine that can send query requests to SNMP agents with the correct credentials. Configure Snmp Windows 7 Cacti Monitoring' title='Configure Snmp Windows 7 Cacti Monitoring' />SNMP Managers key functions queries agents, gets responses from agents, sets variables in agents and acknowledges asynchronous events from agents. Agent theses are softwares which run on managed devices. Pc Tools Registry Mechanic 2010 Honda. They are responsible for gathering information about the local system and storing them in a format that can be queried. MIB. Network management station NMS it executes applications that monitor and control managed devices. MIB is a database that follows a standard that the manager and agents adhere to. Every SNMP agent maintains an information database describing the managed device parameters. The SNMP manager uses this database to request the agent for specific information and further translates the information as needed for the Network Management System NMS. This commonly shared database between the Agent and the Manager is our MIB. SNMP version. Currently, there are 3 versions for SNMP. SNMP Version 1 This provides device statistics and error reporting without consuming a lot of system resources. Security is limited to community strings and access controls based on the IP address of the querying server. Data communication isnt encrypted. SNMP Version 2 This is referred to as v. SNMP Version 3 This version provides greater security and remote configuration capabilities than its predecessors. Access isnt limited to a single community string for read only and readwrite access, as usernames and passwords have been introduced. Support for encrypted SNMP data transfer and transfer error detection is also provided. Installation of snmp. We will present snmp installation both on ubuntu and centos apt get install y snmpd snmp yum install y net snmp net snmp utils. Configuration of SNMPThe configuration file of SNMP service can be found at etcsnmpsnmpd. Before modifying the file, make a copy of the file by the command cp etcsnmpsnmpd. Following are the basic configuration parameters you can use to configure SNMP. Set community string for SNMP it is like a user id or password that allows access to a devices statistics. This string will be used by the client machines to retrieve data to generate monitoring graphs. This is a mandatory configuration parameter. It can be identified where you will see rocommunity . The default value is public which is not secured because everybody know it by default. Listening address We can configure the SNMP agent to listen only to a particular IP address as follows agent. Address udp ipaddress 1. The default port on which SNMP listens is 1. The default behavior of the agent is to listen on standard UDP port on all interfaces. System information it concerns personal infos, processdisk monitoring,syslocation This is the typically physical location of the system. This is the contact information for the administrator. Our modified information should be like below, notice that there are other default values on the file which dont appear here Listen for connections on all interfaces both IPv. IPv. 6. agent. Address udp 1. ACCESS CONTROL. view all included . For a more comprehensive list of monitoring tools and their features, check out this Wikipedia page. As the question states, what are the most commonly used tools. In this howto we are going to show you how to install and setup complete network monitoring application called Cacti using NetSNMP tool on RHELCentOSFedora. Top VIdeos. Warning Invalid argument supplied for foreach in srvusersserverpilotappsjujaitalypublicindex. Default access to basic system info. V all. rocommunity. IPv. 6. rocommunity. V all. sys. Location linoxide. Contact Me lt email protected. ACTIVE MONITORING. Nobody would ever need monitoring software for all kinds of systems if all devices in the world were as hardworking and as trustworthy as yourself. But machines have. Solution This is a complicated question and requires some background knowledge of the various ways of monitoring to be be able to set it up appropriately. Even. Tech Short How To Disable and Enable Ports HP ProCurve. Home Tech Short How To Disable and Enable Ports HP ProCurve. Further Information. Minute IT Managers Guide to Network Visibility series of podcasts from VSS Monitoring covers traffic visibilitys role in network monitoring. This article is intended to guide you with easy instructions on how to install latest Nagios 4. RHEL CentOS 7. x6. Fedora. An interesting article to install and setup Cacti Network Monitoring System on Ubuntu 16. SNMPv. 1 traps. trapsink localhost public. SNMPv. 2c traps. trap. Config. User default mycomm. Make at least snmpwalk v 1 localhost c public system fast again. The SNMP service needs to be restarted for any configuration change etcsnmpsnmpd. This can be accomplished as follows service snmpd restartwith systemd do systemctl restart snmpd. Testing SNMP service. You can test whether SNMP can read the system and interface MIBs using the snmpwalk command. O e 1. 27. 0. 0. 1. Configure Snmp Windows 7 Cacti Monitoring SoftwareSTRING Linux ubuntu 0. Ubuntu SMP Fri Mar 3 1. UTC 2. 01. 7 x. 866. OID iso. 3. 6. 1. Timeticks 1. 54. STRING me lt email protected. STRING ubuntu 0. STRING linoxide. INTEGER 7. 2. iso. Timeticks 1 0 0. OID iso. OID iso. 3. 6. 1. STRING The MIB for Message Processing and Dispatching. L3FqQTlRI/maxresdefault.jpg' alt='Configure Snmp Windows 7 Cacti Monitoring For Windows' title='Configure Snmp Windows 7 Cacti Monitoring For Windows' />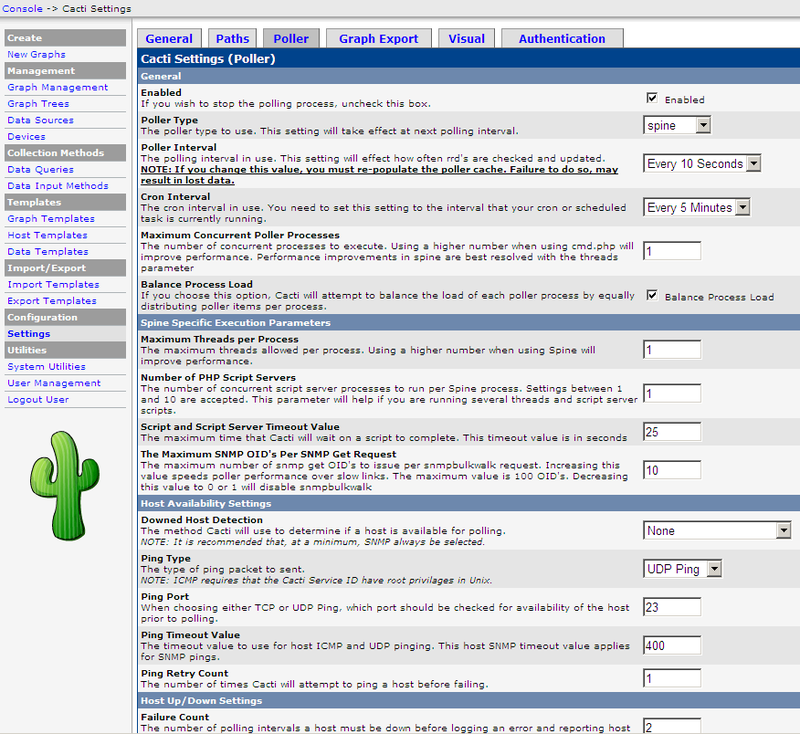 STRING The SNMP Management Architecture MIB. Timeticks 9. 97. Hex STRING 0. E1 0. B 0. 0 0. 0. INTEGER 3. 93. 21. STRING BOOTIMAGEbootvmlinuz 4. LABELcloudimg rootfs ro consoletty. S0. iso. 3. 6. 1. Gauge. 32 1. iso. Gauge. 32 1. 21. INTEGER 0. O e 1. 27. 0. 0. 1. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Descr. 0 STRING Linux centos 0. SMP Wed Jan 1. 8 1. UTC 2. 01. 7 x. 866. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Object. ID. 0 OID NET SNMP MIB net. Snmp. Agent. OIDs. DISMAN EVENT MIB sys. Up. Time. Instance Timeticks 3. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Contact. 0 STRING admin lt email protected configure etcsnmpsnmp. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Name. 0 STRING centos 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Location. 0 STRING centos linoxide. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORLast. Change. 0 Timeticks 8 0 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 1 OID SNMP MPD MIB snmp. MPDCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 2 OID SNMP USER BASED SM MIB usm. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 3 OID SNMP FRAMEWORK MIB snmp. Framework. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 4 OID SNMPv. MIB snmp. MIB. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 5 OID TCP MIB tcp. MIBOnce you have verified that SNMP is working correctly, you can configure SNMP statistics gathering software such as MRTG to create online graphs of your traffic flows. Conclusion. SNMP is used to monitor devices on a network. There are some monitoring tools based on it which are very popular and used across the world. We know the concept of snmp and how it works. With this basic concepts, you are able to use snmp tools to explore this environment. How to monitor Linux servers with SNMP and Cacti. SNMP or Simple Network Management Protocol is used to gather data on what is going on within a device, such as load, hard disk states, bandwidth. These data are used by network monitoring tools such as Cacti to generate graphs for monitoring purposes. In a typical deployment of Cacti and SNMP, there will be one or more SNMP enabled devices, and a separate monitoring server where Cacti collects SNMP feeds from those devices. Please keep in mind that all the devices that need to be monitored must be SNMP enabled. In this tutorial, we will be configuring Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server for demonstration purpose. Configure SNMP on Debian or Ubuntu. To install SNMP agent snmpd on a Debian based system, run the following command. Then edit its configuration like the following. Address udp 1. 61. Community and the source network is defined. Community 1. 72. 1. Location Earth. sys. Contact emaildomain. After editing the config file, restart snmpd. Configure SNMP on Cent. OS or RHELTo install SNMP tools and libraries, run the following command. Then edit an SNMP config file like the following. A user my. User is being defined with the community string my. Community and source network 1. User 1. 72. 1. 7. Community. my. User is added into the group my. Group and the permission of the group is defined. Group v. 1 my. User. Group v. User. view all included. Group any noauth exact all all none. Restart snmpd service, and add it to startup service list. Testing SNMPSNMP can be tested by running the snmpwalk command. If SNMP has been successfully configured, this command will generate a ton of output. Community 1. 72. 1. STRING Linux mrtg 3. Ubuntu SMP Tue Oct 9 1. UTC 2. 01. 2 x. 866. OID iso. 3. 6. 1. Timeticks 2. 09. OUTPUT TRUNCATED. Gauge. 32 1. 44. Counter. Counter. 32 0. iso. Timeticks 1 0 0. Hex STRING 0. DD 0. B 1. 2 0. 0 3. B 0. 6 0. 0. Configure Cacti with SNMPIn this tutorial, we are setting up both Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server. So go ahead and install Cacti on your Linux server on which SNMP was just configured. After installation, Cacti web interface can be accessed using the link http 1. IP address of your server. The paths during Cacti installation are usually correct. But they can be double checked if necessary. During the first time installation, the default username and password for Cacti are admin and admin. You will be forced to change the password after first login. Add and Manage Devices to Cacti. Cacti will poll devices based on SNMP string that was configured earlier. In this tutorial, we will add only the local server where SNMP is already enabled. To add devices, we login as admin and go to console in the Cacti admin panel. We click Console Devices. There may already be a device named localhost. We do not need it as we will create fresh graphs. We can delete this device from the list. We add a new device by using the add button. Next, we set the device parameters. Now that the device has been added, we specify the graph templates that we want to create. This section can be found in the bottom section of the page. And then we proceed to creating the graphs. Here, we create graphs for load average, RAM and hard disk, processor. Interface Graphs and 6. Counters. By default, Cacti uses 3. SNMP queries. 3. 2 bit counters are sufficient for most bandwidth graphs, but they do not work correctly for graphs greater than 1. Mbps. If it is known that the bandwidth will exceed more than 1. Mbps, it is always advisable to use 6. Using 6. 4 bit counters is not hard at all. Note It takes around 1. Cacti to populate new graphs. There are not alternatives to being patient. Creating Graph Trees. These snapshots illustrate how to create graph trees and how to add graph to those trees. We can verify the graph in the graph tree. User Management. Finally, we create a user with view permission to only the graph that we have created. Cacti has built in user management system, and it is highly customizable. After completing these steps, we can log in with the user user. And thus we have deployed a Cacti server in the network monitoring system. Cacti servers are stable, and can deal with tons of graphs without any problems.
STRING The SNMP Management Architecture MIB. Timeticks 9. 97. Hex STRING 0. E1 0. B 0. 0 0. 0. INTEGER 3. 93. 21. STRING BOOTIMAGEbootvmlinuz 4. LABELcloudimg rootfs ro consoletty. S0. iso. 3. 6. 1. Gauge. 32 1. iso. Gauge. 32 1. 21. INTEGER 0. O e 1. 27. 0. 0. 1. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Descr. 0 STRING Linux centos 0. SMP Wed Jan 1. 8 1. UTC 2. 01. 7 x. 866. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Object. ID. 0 OID NET SNMP MIB net. Snmp. Agent. OIDs. DISMAN EVENT MIB sys. Up. Time. Instance Timeticks 3. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Contact. 0 STRING admin lt email protected configure etcsnmpsnmp. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Name. 0 STRING centos 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Location. 0 STRING centos linoxide. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORLast. Change. 0 Timeticks 8 0 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 1 OID SNMP MPD MIB snmp. MPDCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 2 OID SNMP USER BASED SM MIB usm. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 3 OID SNMP FRAMEWORK MIB snmp. Framework. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 4 OID SNMPv. MIB snmp. MIB. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 5 OID TCP MIB tcp. MIBOnce you have verified that SNMP is working correctly, you can configure SNMP statistics gathering software such as MRTG to create online graphs of your traffic flows. Conclusion. SNMP is used to monitor devices on a network. There are some monitoring tools based on it which are very popular and used across the world. We know the concept of snmp and how it works. With this basic concepts, you are able to use snmp tools to explore this environment. How to monitor Linux servers with SNMP and Cacti. SNMP or Simple Network Management Protocol is used to gather data on what is going on within a device, such as load, hard disk states, bandwidth. These data are used by network monitoring tools such as Cacti to generate graphs for monitoring purposes. In a typical deployment of Cacti and SNMP, there will be one or more SNMP enabled devices, and a separate monitoring server where Cacti collects SNMP feeds from those devices. Please keep in mind that all the devices that need to be monitored must be SNMP enabled. In this tutorial, we will be configuring Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server for demonstration purpose. Configure SNMP on Debian or Ubuntu. To install SNMP agent snmpd on a Debian based system, run the following command. Then edit its configuration like the following. Address udp 1. 61. Community and the source network is defined. Community 1. 72. 1. Location Earth. sys. Contact emaildomain. After editing the config file, restart snmpd. Configure SNMP on Cent. OS or RHELTo install SNMP tools and libraries, run the following command. Then edit an SNMP config file like the following. A user my. User is being defined with the community string my. Community and source network 1. User 1. 72. 1. 7. Community. my. User is added into the group my. Group and the permission of the group is defined. Group v. 1 my. User. Group v. User. view all included. Group any noauth exact all all none. Restart snmpd service, and add it to startup service list. Testing SNMPSNMP can be tested by running the snmpwalk command. If SNMP has been successfully configured, this command will generate a ton of output. Community 1. 72. 1. STRING Linux mrtg 3. Ubuntu SMP Tue Oct 9 1. UTC 2. 01. 2 x. 866. OID iso. 3. 6. 1. Timeticks 2. 09. OUTPUT TRUNCATED. Gauge. 32 1. 44. Counter. Counter. 32 0. iso. Timeticks 1 0 0. Hex STRING 0. DD 0. B 1. 2 0. 0 3. B 0. 6 0. 0. Configure Cacti with SNMPIn this tutorial, we are setting up both Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server. So go ahead and install Cacti on your Linux server on which SNMP was just configured. After installation, Cacti web interface can be accessed using the link http 1. IP address of your server. The paths during Cacti installation are usually correct. But they can be double checked if necessary. During the first time installation, the default username and password for Cacti are admin and admin. You will be forced to change the password after first login. Add and Manage Devices to Cacti. Cacti will poll devices based on SNMP string that was configured earlier. In this tutorial, we will add only the local server where SNMP is already enabled. To add devices, we login as admin and go to console in the Cacti admin panel. We click Console Devices. There may already be a device named localhost. We do not need it as we will create fresh graphs. We can delete this device from the list. We add a new device by using the add button. Next, we set the device parameters. Now that the device has been added, we specify the graph templates that we want to create. This section can be found in the bottom section of the page. And then we proceed to creating the graphs. Here, we create graphs for load average, RAM and hard disk, processor. Interface Graphs and 6. Counters. By default, Cacti uses 3. SNMP queries. 3. 2 bit counters are sufficient for most bandwidth graphs, but they do not work correctly for graphs greater than 1. Mbps. If it is known that the bandwidth will exceed more than 1. Mbps, it is always advisable to use 6. Using 6. 4 bit counters is not hard at all. Note It takes around 1. Cacti to populate new graphs. There are not alternatives to being patient. Creating Graph Trees. These snapshots illustrate how to create graph trees and how to add graph to those trees. We can verify the graph in the graph tree. User Management. Finally, we create a user with view permission to only the graph that we have created. Cacti has built in user management system, and it is highly customizable. After completing these steps, we can log in with the user user. And thus we have deployed a Cacti server in the network monitoring system. Cacti servers are stable, and can deal with tons of graphs without any problems.
 STRING The SNMP Management Architecture MIB. Timeticks 9. 97. Hex STRING 0. E1 0. B 0. 0 0. 0. INTEGER 3. 93. 21. STRING BOOTIMAGEbootvmlinuz 4. LABELcloudimg rootfs ro consoletty. S0. iso. 3. 6. 1. Gauge. 32 1. iso. Gauge. 32 1. 21. INTEGER 0. O e 1. 27. 0. 0. 1. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Descr. 0 STRING Linux centos 0. SMP Wed Jan 1. 8 1. UTC 2. 01. 7 x. 866. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Object. ID. 0 OID NET SNMP MIB net. Snmp. Agent. OIDs. DISMAN EVENT MIB sys. Up. Time. Instance Timeticks 3. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Contact. 0 STRING admin lt email protected configure etcsnmpsnmp. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Name. 0 STRING centos 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Location. 0 STRING centos linoxide. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORLast. Change. 0 Timeticks 8 0 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 1 OID SNMP MPD MIB snmp. MPDCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 2 OID SNMP USER BASED SM MIB usm. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 3 OID SNMP FRAMEWORK MIB snmp. Framework. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 4 OID SNMPv. MIB snmp. MIB. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 5 OID TCP MIB tcp. MIBOnce you have verified that SNMP is working correctly, you can configure SNMP statistics gathering software such as MRTG to create online graphs of your traffic flows. Conclusion. SNMP is used to monitor devices on a network. There are some monitoring tools based on it which are very popular and used across the world. We know the concept of snmp and how it works. With this basic concepts, you are able to use snmp tools to explore this environment. How to monitor Linux servers with SNMP and Cacti. SNMP or Simple Network Management Protocol is used to gather data on what is going on within a device, such as load, hard disk states, bandwidth. These data are used by network monitoring tools such as Cacti to generate graphs for monitoring purposes. In a typical deployment of Cacti and SNMP, there will be one or more SNMP enabled devices, and a separate monitoring server where Cacti collects SNMP feeds from those devices. Please keep in mind that all the devices that need to be monitored must be SNMP enabled. In this tutorial, we will be configuring Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server for demonstration purpose. Configure SNMP on Debian or Ubuntu. To install SNMP agent snmpd on a Debian based system, run the following command. Then edit its configuration like the following. Address udp 1. 61. Community and the source network is defined. Community 1. 72. 1. Location Earth. sys. Contact emaildomain. After editing the config file, restart snmpd. Configure SNMP on Cent. OS or RHELTo install SNMP tools and libraries, run the following command. Then edit an SNMP config file like the following. A user my. User is being defined with the community string my. Community and source network 1. User 1. 72. 1. 7. Community. my. User is added into the group my. Group and the permission of the group is defined. Group v. 1 my. User. Group v. User. view all included. Group any noauth exact all all none. Restart snmpd service, and add it to startup service list. Testing SNMPSNMP can be tested by running the snmpwalk command. If SNMP has been successfully configured, this command will generate a ton of output. Community 1. 72. 1. STRING Linux mrtg 3. Ubuntu SMP Tue Oct 9 1. UTC 2. 01. 2 x. 866. OID iso. 3. 6. 1. Timeticks 2. 09. OUTPUT TRUNCATED. Gauge. 32 1. 44. Counter. Counter. 32 0. iso. Timeticks 1 0 0. Hex STRING 0. DD 0. B 1. 2 0. 0 3. B 0. 6 0. 0. Configure Cacti with SNMPIn this tutorial, we are setting up both Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server. So go ahead and install Cacti on your Linux server on which SNMP was just configured. After installation, Cacti web interface can be accessed using the link http 1. IP address of your server. The paths during Cacti installation are usually correct. But they can be double checked if necessary. During the first time installation, the default username and password for Cacti are admin and admin. You will be forced to change the password after first login. Add and Manage Devices to Cacti. Cacti will poll devices based on SNMP string that was configured earlier. In this tutorial, we will add only the local server where SNMP is already enabled. To add devices, we login as admin and go to console in the Cacti admin panel. We click Console Devices. There may already be a device named localhost. We do not need it as we will create fresh graphs. We can delete this device from the list. We add a new device by using the add button. Next, we set the device parameters. Now that the device has been added, we specify the graph templates that we want to create. This section can be found in the bottom section of the page. And then we proceed to creating the graphs. Here, we create graphs for load average, RAM and hard disk, processor. Interface Graphs and 6. Counters. By default, Cacti uses 3. SNMP queries. 3. 2 bit counters are sufficient for most bandwidth graphs, but they do not work correctly for graphs greater than 1. Mbps. If it is known that the bandwidth will exceed more than 1. Mbps, it is always advisable to use 6. Using 6. 4 bit counters is not hard at all. Note It takes around 1. Cacti to populate new graphs. There are not alternatives to being patient. Creating Graph Trees. These snapshots illustrate how to create graph trees and how to add graph to those trees. We can verify the graph in the graph tree. User Management. Finally, we create a user with view permission to only the graph that we have created. Cacti has built in user management system, and it is highly customizable. After completing these steps, we can log in with the user user. And thus we have deployed a Cacti server in the network monitoring system. Cacti servers are stable, and can deal with tons of graphs without any problems.
STRING The SNMP Management Architecture MIB. Timeticks 9. 97. Hex STRING 0. E1 0. B 0. 0 0. 0. INTEGER 3. 93. 21. STRING BOOTIMAGEbootvmlinuz 4. LABELcloudimg rootfs ro consoletty. S0. iso. 3. 6. 1. Gauge. 32 1. iso. Gauge. 32 1. 21. INTEGER 0. O e 1. 27. 0. 0. 1. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Descr. 0 STRING Linux centos 0. SMP Wed Jan 1. 8 1. UTC 2. 01. 7 x. 866. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Object. ID. 0 OID NET SNMP MIB net. Snmp. Agent. OIDs. DISMAN EVENT MIB sys. Up. Time. Instance Timeticks 3. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Contact. 0 STRING admin lt email protected configure etcsnmpsnmp. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Name. 0 STRING centos 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. Location. 0 STRING centos linoxide. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORLast. Change. 0 Timeticks 8 0 0. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 1 OID SNMP MPD MIB snmp. MPDCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 2 OID SNMP USER BASED SM MIB usm. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 3 OID SNMP FRAMEWORK MIB snmp. Framework. MIBCompliance. SNMPv. 2 MIB sys. ORID. 4 OID SNMPv. MIB snmp. MIB. SNMPv. MIB sys. ORID. 5 OID TCP MIB tcp. MIBOnce you have verified that SNMP is working correctly, you can configure SNMP statistics gathering software such as MRTG to create online graphs of your traffic flows. Conclusion. SNMP is used to monitor devices on a network. There are some monitoring tools based on it which are very popular and used across the world. We know the concept of snmp and how it works. With this basic concepts, you are able to use snmp tools to explore this environment. How to monitor Linux servers with SNMP and Cacti. SNMP or Simple Network Management Protocol is used to gather data on what is going on within a device, such as load, hard disk states, bandwidth. These data are used by network monitoring tools such as Cacti to generate graphs for monitoring purposes. In a typical deployment of Cacti and SNMP, there will be one or more SNMP enabled devices, and a separate monitoring server where Cacti collects SNMP feeds from those devices. Please keep in mind that all the devices that need to be monitored must be SNMP enabled. In this tutorial, we will be configuring Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server for demonstration purpose. Configure SNMP on Debian or Ubuntu. To install SNMP agent snmpd on a Debian based system, run the following command. Then edit its configuration like the following. Address udp 1. 61. Community and the source network is defined. Community 1. 72. 1. Location Earth. sys. Contact emaildomain. After editing the config file, restart snmpd. Configure SNMP on Cent. OS or RHELTo install SNMP tools and libraries, run the following command. Then edit an SNMP config file like the following. A user my. User is being defined with the community string my. Community and source network 1. User 1. 72. 1. 7. Community. my. User is added into the group my. Group and the permission of the group is defined. Group v. 1 my. User. Group v. User. view all included. Group any noauth exact all all none. Restart snmpd service, and add it to startup service list. Testing SNMPSNMP can be tested by running the snmpwalk command. If SNMP has been successfully configured, this command will generate a ton of output. Community 1. 72. 1. STRING Linux mrtg 3. Ubuntu SMP Tue Oct 9 1. UTC 2. 01. 2 x. 866. OID iso. 3. 6. 1. Timeticks 2. 09. OUTPUT TRUNCATED. Gauge. 32 1. 44. Counter. Counter. 32 0. iso. Timeticks 1 0 0. Hex STRING 0. DD 0. B 1. 2 0. 0 3. B 0. 6 0. 0. Configure Cacti with SNMPIn this tutorial, we are setting up both Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server. So go ahead and install Cacti on your Linux server on which SNMP was just configured. After installation, Cacti web interface can be accessed using the link http 1. IP address of your server. The paths during Cacti installation are usually correct. But they can be double checked if necessary. During the first time installation, the default username and password for Cacti are admin and admin. You will be forced to change the password after first login. Add and Manage Devices to Cacti. Cacti will poll devices based on SNMP string that was configured earlier. In this tutorial, we will add only the local server where SNMP is already enabled. To add devices, we login as admin and go to console in the Cacti admin panel. We click Console Devices. There may already be a device named localhost. We do not need it as we will create fresh graphs. We can delete this device from the list. We add a new device by using the add button. Next, we set the device parameters. Now that the device has been added, we specify the graph templates that we want to create. This section can be found in the bottom section of the page. And then we proceed to creating the graphs. Here, we create graphs for load average, RAM and hard disk, processor. Interface Graphs and 6. Counters. By default, Cacti uses 3. SNMP queries. 3. 2 bit counters are sufficient for most bandwidth graphs, but they do not work correctly for graphs greater than 1. Mbps. If it is known that the bandwidth will exceed more than 1. Mbps, it is always advisable to use 6. Using 6. 4 bit counters is not hard at all. Note It takes around 1. Cacti to populate new graphs. There are not alternatives to being patient. Creating Graph Trees. These snapshots illustrate how to create graph trees and how to add graph to those trees. We can verify the graph in the graph tree. User Management. Finally, we create a user with view permission to only the graph that we have created. Cacti has built in user management system, and it is highly customizable. After completing these steps, we can log in with the user user. And thus we have deployed a Cacti server in the network monitoring system. Cacti servers are stable, and can deal with tons of graphs without any problems.